With the recent publicity given to cyber-attacks, Kingdom has put together some basic advice to help you stay safe on the internet.
With the recent publicity given to cyber-attacks, Kingdom has put together some basic advice to help you stay safe on the internet.
The creation of the internet was one of the biggest achievements of the 20th century, and now in the 21st century it is becoming an integral part of our lives from shopping and interacting on social media to streaming TV shows and movies. Almost all of us now go online every day, but beware! The more we use the internet to aid us, the more criminals will look to use the internet against us.
Below are some tips to help you stay one step ahead.
Phishing
Phishing is one of the ways fraudsters try to trick people into revealing confidential or personal information. Phishing is basically an email that looks genuine, like it's from your bank or from us, asking you to divulge personal information on an unsecure site.
There are a few top tips to help you spot a phishing email:
- Check the email address - is it the same as the address you would normally receive your emails from? Pay extra attention to the words after the @ symbol. Most reputable companies will have the company name after the @ symbol, for example paul@kingdom.co.uk. Email addresses from free providers such as @hotmail, @gmail @outlook etc can be setup by anyone anonymously so be particularly wary of these.
- Check the subject line and treat emails which create a sense of urgency as suspicious e.g. "security alert" or "if you do not reply in 48 hours your account will be suspended."
- Check the message title — be suspicious of emails that aren't addressed personally to you by name, and say something like “Dear customer” or “Dear valued customer”.
- Be suspicious of emails which ask you to reply with personal information that a genuine company would not ask you for, such as usernames, passwords, your date of birth or card details. Remember no bank or building society will ever ask you to write down passwords or PIN numbers in emails.
- Be suspicious of anyone emailing to ask for payment for processing or administration, especially those that ask for payment in ukash vouchers or bitcoin. These are legitimate payment systems but scammers like to use them because they provide anonymity to the recipient.
- Check the address of any links within the email — treat emails as suspicious if there are links to other websites to make a payment or confirm your details. DON'T click the link or input any details. Go directly to the website.
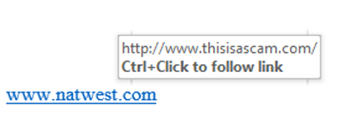
- You can hover your mouse pointer over hyperlinks (or buttons) to see the underlying website address (URL). If the address does not match the website you would normally associate with the company claiming to be contacting you then do not click the link. For example, below, what looks like a link to www.natwest.com is actually a link to www.thisisascam.com even though the text says Natwest.
If you do follow a link without checking it like above look at the address bar at the top of the screen to ensure you are on the correct page.
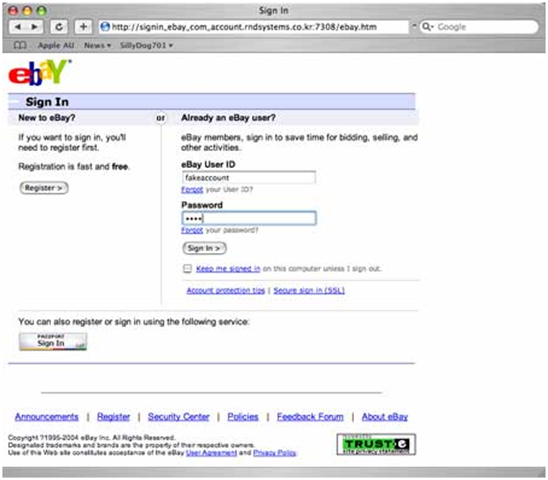
The below website looks just like eBay:
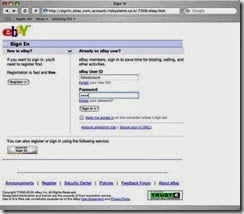 |
|
However if you look at the address at the top: |
|
The address should be:
On the fake website they have used _ instead of . for the ebay address.
Passwords
Putting a password on something will make it harder to get into, but how strong are your passwords?
Here are some guidelines to create stronger passwords.
- Pick longer passwords, at least 8 characters in length (the longer the better) if the system allows it.
- Try to avoid using common dictionary words, a name, or a string of numbers.
- Include random capital letters. Most passwords are case sensitive so put a capital letter where you wouldn’t expect to find one. For example, with the word security, if you use capital letters on letters other than the first (SecUrITy) the password becomes harder to break.
- Try to include numbers or special characters ($ . , ! % ^ *) where possible in your passwords. It’s not as hard as it sounds! Again, for example if you take the word security and replace the S with a $ and the I with a 1 you get $ecur1ty, and you have just increased the strength of your password!
One of the easiest to remember and hardest to crack password methods is the pseudo-random password. The actual password is generated from an easy to remember phrase that is important to the user. This phrase can be the words from a book that you particularly like, words from a song that you always remember with ease, or a statement that some powerful figure made that you will never forget. The key to a successful password is to create a phrase that is easy for you to remember, but no one else will ever think about attributing it to you.
E.g. ‘One small step for man one giant leap for mankind’ would become = Ossfmoglfm
Due to the pseudo randomness of the letters it makes it harder to crack. If you wanted to take it a step further you could include the other steps listed above so:
Ossfmoglfm could become 0$$fM0glFm
This password is:
- Longer than 8 characters
- Avoided common words
- Includes random capitalisation
- Uses numbers and symbols
In summary, it is a very complex password and would be incredibly difficult to crack.
One final point – even the most complicated password won’t protect you if you give it out to other people. This may sound obvious but ask yourself, if I were to ask you for the PIN number to unlock your mobile phone would you give it to me?
Then ask yourself, if I were to ask you for the PIN number for your debit card would you give it to me?
Most people will answer yes to the first question and no to the second question. The problem with that is that at least half of those people will be using the same PIN number for both.